Everyone who has been involved with IT for more than a few months has at least heard of MySQL. The acquisition of MySQL AB by Sun Microsystems brought a great deal of additional attention to MySQL’s database management system (DBMS). Even so, there is often more to MySQL than many people realize.
Unix-based servers with MySQL installations represent the majority of current installations of MySQL Server. Unlike Windows, Unix-based servers come in a number of packaging formats and configurations.
Suggested Read: Handy MySQL Commands – Cheatsheet 2018
And it is often required to get the size of a database in MYSQL via command line if you are using UNIX based OS.
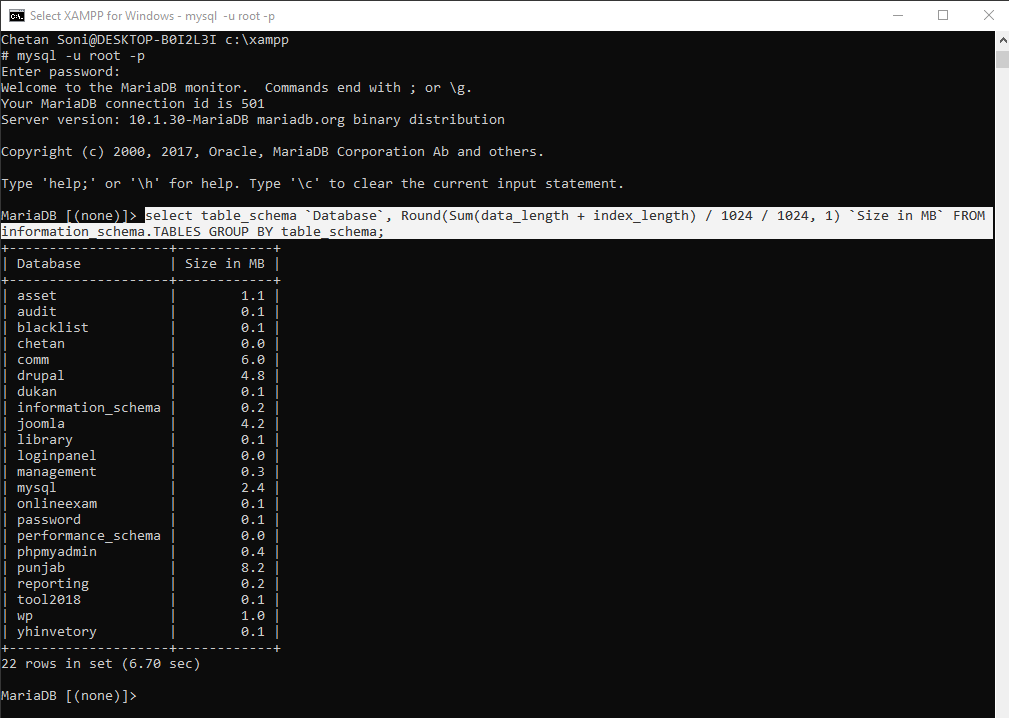
By just a single SQL Query, you can easily get the information about the required databases from information_schema and print their size in MBs with the following command:
Command: select table_schema `Database`, Round(Sum(data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024, 1) `Size in MB` FROM information_schema.TABLES GROUP BY table_schema;
In case, if you want to display the DB size of a particular database, then use the following command:
Command: select table_schema `Database`, Round(Sum(data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024, 1) `Size in MB` FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = ‘drupal’;

Similarly you can also find out the size of a particular table by typing the following command:
Command: SELECT table_name AS `Table`, round(((data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024), 2) `Size in MB` FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = “wp” AND table_name = “wp_users”;