
Anyone can, with the right equipment, access wireless networks (wireless local area networks, wlan’s). After all, there is no physical barrier that makes break-in attempts more difficult, as is the case with wired networks. Wireless networks therefore impose different requirements on security than wired.
There are four types of security intrusions (or intrusions) on computer networks: the intrusion with physical access, the intrusion with system access, the remote intrusion and the wireless intrusion. The latter is a special case. It shows characteristics of the three other types. Only the intrusion happens wirelessly and therefore potentially without you noticing it.
Below you can find the best wireless penetration testing tools which are as follows:
1. Aircrack-ng
Aircrack-ng is a complete set of tools to access or test the Wi-Fi Network Security which focuses on mainly Monitoring, Attacking, Testing and Cracking. In every Kali Linux versions, you can found Aircrack-ng pre-installed in it. The latest version of Aircrack-ng is 1.2 RC 4.
If you are using some other Linux distribution just like Ubuntu/Fedora, then you can easily download Aircrack from their official website.
Installation Instructions for Linux Distributions –
wget http://download.aircrack-ng.org/aircrack-ng-1.2-rc4.tar.gz
tar -zxvf aircrack-ng-1.2-rc4.tar.gz
cd aircrack-ng-1.2-rc4
make
make install
Aircrack-ng Suite includes:
- airbase-ng – Multi-purpose tool aimed at attacking clients as opposed to the Access Point (AP) itself.
- aircrack-ng – 802.11 WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK key cracking program.
- airdecap-ng – Decrypt WEP/WPA/WPA2 capture files.
- airdecloak-ng – Remove WEP Cloaking™ from a packet capture file.
- airdrop-ng – A rule based wireless deauthication tool.
- aireplay-ng – Inject and replay wireless frames.
- airgraph-ng – Graph wireless networks.
- airmon-ng – Enable and disable monitor mode on wireless interfaces.
- airodump-ng – Capture raw 802.11 frames.
- airolib-ng – Precompute WPA/WPA2 passphrases in a database to use it later with aircrack-ng.
- airserv-ng – Wireless card TCP/IP server which allows multiple application to use a wireless card.
- airtun-ng – Virtual tunnel interface creator.
- packetforge-ng – Create various type of encrypted packets that can be used for injection.

By typing aircrack-ng in the shell you will discover the different options available. For this type of crack, the basic command is:
Syntax – aircrack-ng capture-file-name.cap
The aircrack-ng suite is constantly evolving and new versions are coming out often, bringing improvements. Unfortunately, the Linux versions are less frequent. But recently, a new crack algorithm has emerged through which you can crack WEP key with 40000 Ivs (instead of 1 000 000!), It is about aircrack-ptw whose features are implemented in the latest version of aircrack-ng.
2. Kismet
Kismet Wireless is a free open source network detector, packet multiplier and intrusion detection system for wireless networks based on the IEEE 802.11x standards. It works on Linux and other Unix variants like BSD and Mac OS X.
In terms of hardware you need a wireless network card. It must be able to work promiscuously and thus also receive strange network packages. Kismet supports around 20 wlan cards.
Official Website Link – https://www.kismetwireless.net/
Unlike other wlan detection systems, Kismet operates purely passively. It only works on the basis of what the Wlan card can receive.

Features of Kismet –
- Kismet can associate the found AP’s and clients. This way you can see who is trying to make contact with whom.
- Kismet can detect break-in attempts via the broadcast network packages. It thus offers basic IDS functionality (intrusion detection).
- Kismet can also discover competitive sniffers such as NetStumbler as long as they are active and not – like
- Kismet itself – passively.
- Kismet supports the storage of ‘snapped’ packages in standard formats such as Airsnort and tcpdump / Wireshark.
- To detect as many wireless networks as possible, Kismet supports ‘channel hopping’. Instead of navigating sequentially from one channel to the next, Kismet hopped back and forth between channels in random order.
- Finally, Kismet can determine the geographical location of a wireless network if you connect a GPS receiver.
3. Reaver
Reaver performs a brute force attack against an access point’s WiFi Protected Setup pin number. Once the WPS pin is found, the WPA PSK can be recovered and alternately the AP’s wireless settings can be reconfigured.
While Reaver does not support reconfiguring the AP, this can be accomplished with wpa_supplicant once the WPS pin is known. Reaver is only supported on the Linux platform, requires the libpcap and libsqlite3 libraries, and can be built and installed by running:
$ ./configure $ make # make install
# make distclean
- Usage: reaver -i wlan0mon -b <Bssid>
You can even define the channel number wrt to Essid
- Usage : reaver -i wlan0mon -b <Bssid> -c 11 -e <Essid>
The default receive timeout period is 5 second which you can easily set by the following command:
- Usage: reaver -i wlan0mon -b <Bssid> -t 2
For additional output, the verbose option may be set by using -vv at the end of the command
- Usage: reaver -i wlan0mon -b <Bssid> -vv
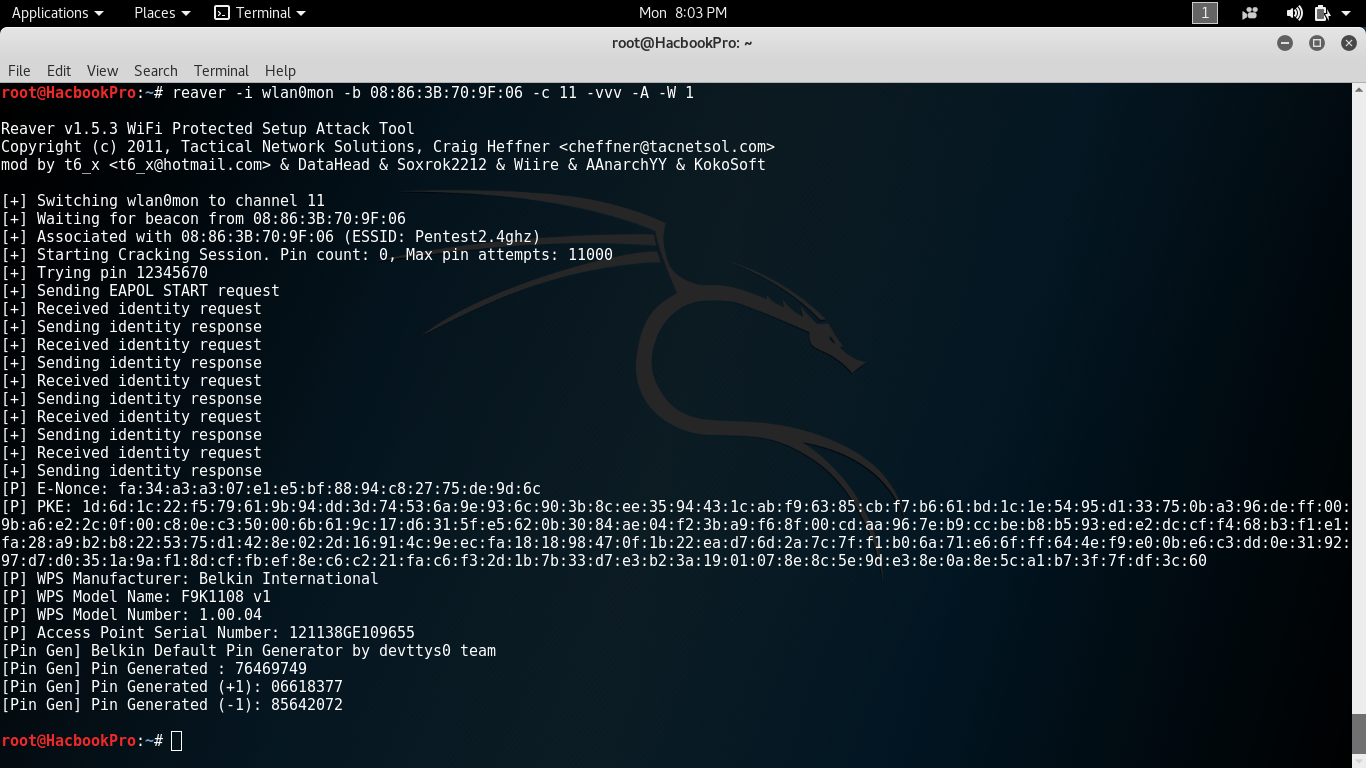
Current attacks against WPA networks use rainbow tables based on potential key wordings and the name (SSID) of the network to attack. In addition, the rainbow table must be regenerated for each network. Reaver would not have to deal with these limitations. Reaver can get the WPA PSK out of the access point within four to ten hours and roughly 95% of the consumer access points are supplied with WPA as standard.
4. Wifite
Wifite is an automated wireless attacking tool through which we can easily hack/crack the wireless network key. Basically there are two versions are available i.e. Wifite (v1) and Wifite2 (v2).
Wifite was designed for use with pentesting distributions of Linux, such as Kali Linux, Pentoo, BackBox; any Linux distributions with wireless drivers patched for injection. The script appears to also operate with Ubuntu 11/10, Debian 6, and Fedora 16.

Wifite assumes that you have a wireless card and the appropriate drivers that are patched for injection and promiscuous/monitor mode.
Download & Execute Wifite from Github –
wget https://raw.github.com/derv82/wifite/master/wifite.py
chmod +x wifite.py
./wifite.py
Wifite 2 – An advanced version of Wifite (v1) with cleaner process management which is only designed entirely for the latest version of Kali Rolling release.
Features of Wifite2 –
- Reaver Pixie-Dust attack (–pixie)
- Reaver WPS PIN attack (–reaver)
- WPA handshake capture (–no-reaver)
- Validates handshakes against pyrit, tshark, cowpatty, and aircrack-ng
- Various WEP attacks (replay, chopchop, fragment, etc)
- 5Ghz support for wireless cards that support 5ghz (use -5 option)
- Stores cracked passwords and handshakes to the current directory, with metadata about the access point (via –cracked command).
- Decloaks hidden access points when channel is fixed (use -c <channel> option)
- Provides commands to crack captured WPA handshakes (via –crack command)
Download & Execute Wifite2 from Github –
git clone https://github.com/derv82/wifite2.git
cd wifite2
./Wifite.py
5. Fluxion
Fluxion is Suite of automated social engineering based WPA/WPA2 attacks or you can call as a Wireless Phishing Tool.

Fluxion is intended to be used for legal security purposes only, and you should only use it to protect networks/hosts you own or have permission to test. Any other use is not the responsibility of the developer(s). Be sure that you understand and are complying with the Fluxion licenses and laws in your area.
For more info about Fluxion, please go to Wi-Fi Cracking WPA2-PSK with Fluxion.
You may also like:- How Paraphrase Tool Helps To Optimize Content
- Best 20 Kali Linux Tools for Hacking and Penetration Testing
- Top 25 Open Source Intelligence Tools
- Online Domain Authority (DA) Rank Checker Websites
- Top 50 Hacking and Penetration Testing Tools [Compiled List 2019]
- Top 10 Essential CTF Tools for Solving Reversing Challenges
- Windows and Linux Privilege Escalation Tools – Compiled List 2019
- Subdomain Enumeration Tools – 2019 Update
- Top 10 Most Popular Bruteforce Hacking Tools – 2019 Update
- Top 22 Tools for Solving Steganography Challenges








